The Bluetooth wireless communication range is short, or the sound skips.
- Set the headset to the “Priority on stable connection” mode. For details, refer to “About the sound quality mode.”
-
Remove any obstacles between the antenna of the Bluetooth device to be connected and the built-in antenna of the headset. The antenna of the headset is built into the part shown in the dotted line below.
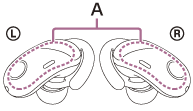
A: Location of the built-in antenna
-
Bluetooth communications may be disabled, or noise or audio dropout may occur under the following conditions.
- When there is a human body between the headset and the Bluetooth device
Put the Bluetooth device in the same direction as the antenna of the headset to improve the Bluetooth communications. - There is an obstacle, such as metal or a wall, between the headset and the Bluetooth device.
- In places with wireless LAN, where a microwave oven is used, electromagnetic waves are generated, etc.
- When there is a human body between the headset and the Bluetooth device
- The situation may be improved by changing the wireless playback quality settings or fixing the wireless playback mode to SBC on the transmitting device. For details, refer to the operating instructions supplied with the transmitting device.
- Because Bluetooth devices and Wi-Fi (IEEE802.11b/g/n) use the same frequency (2.4 GHz), microwave interference may occur resulting in noise or audio dropout or communications being disabled if this headset is used near a Wi-Fi device. In such a case, perform the following.
- Use this headset at least 10 m (30 feet) away from the Wi-Fi device.
- If this headset is used within 10 m (30 feet) of a Wi-Fi device, turn off the Wi-Fi device.
- Install this headset and the Bluetooth device as near to each other as possible.
- If you are enjoying music with your smartphone, the situation may be improved by shutting down unnecessary apps or restarting your smartphone.

