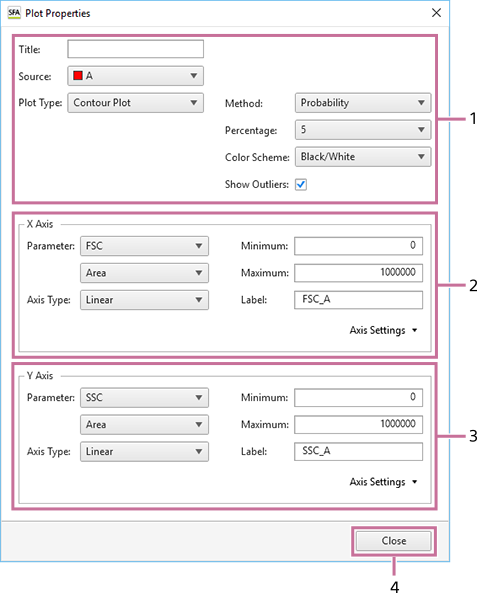
[Plot Properties] Dialog (Properties for Contour Plots)
The [Plot Properties] dialog displays information about the selected plot. You can change the setting of each parameter, as required.
The [Plot Properties] dialog is displayed by clicking  of [Edit] or right-clicking a plot and selecting [Properties].
of [Edit] or right-clicking a plot and selecting [Properties].
-
Basic information
Displays the following information. You can change the settings, as required.
[Title]
Title of the plot.
[Source]
Population of the plot (parent gate).
[Plot Type]
Type of plot.
[Method]
Division method.
- [Probability]: Draw contour lines so that each area between contour lines contains the same number of events.
- [Linear]: Draw contour lines so that each area between contour lines contains the maximum density divided linearly.
- [Log]: Draw contour lines so that each area between contour lines contains the maximum density divided logarithmically.
[Percentage]
Percentage division of the contour lines. The larger the number, the larger the distance between contour lines.
[Color Scheme]
Contour colors.
- [Multicolor]: High-density contour lines are shown in red, and low-density contour lines are shown in blue.
- [Black/White]: Display in black and white.
[Show Outliers]
Place a check mark here to display outlier events outside the outermost contour lines as dots.
-
[X Axis]
Displays information about the X axis of the plot. You can change the settings, as required.
[Parameter]
Parameter.
[Axis Type]
Type of axis.
- Linear: Performs a linear transformation between the acquisition values and the channel numbers (bins) used to acquire data (0 to 256). Linear scales are typically used to display forward scatter and back scatter parameters on plots.
- Log: Display cells that exhibit fluorescence with intensities across a wide dynamic range. Log scales help to make individual peaks easier to visualize. However, log scales cannot adequately represent data with a low mean and high variance.
- Bi-exponential: Combination of a linear scale at the lower end of the axis (around zero) and a logarithmic scale at the higher end of the axis, with an algorithmic transition between the two scales. A biexponential scale allows events close to or below zero to be plotted.
[Minimum]
Minimum value of the scale.
[Maximum]
Maximum value of the scale.
[Label]
Axis label displayed on the graph.
[Axis Settings]
Clicking [Save as Preference Settings] saves the current state as preference settings.
-
[Y Axis]
Displays information about the Y axis of the plot.
For details about each item, see [X Axis].
-
[Close]
Closes the dialog.

